Tätigkeitsbereiche Vom
Geschäftsplan,
Marketing bis zum Controlling
NEU: Überprüfen der Marktstrategie im In- und Ausland - 2,5 Tage intensiv
Exportberatung - Export - Coaching
>>>> Übersicht <<<<< Leistungen und Fachthemen
Interimsmanagement
Teilzeitmanagement
Export Internationales Marketing als Chance
Planung
ist der halbe Erfolg
-
Gestaltung der Planung
Der Nutzen für Klienten Der Berater; Partner und Teil der Untrernehmensführung
© RIETHER, A-3620 Spitz/ Donau
Click+Get® und fascination® sind geschützte Marken
Die Weitergabe oder Verwendung der Inhalte oder Teile bedarf der Zustimmung des Verfassers
CRT Model - Cultural factors determining cooperative activities
Keywords: Cooperation, cultural factors, CRT
The CRT model is a theoretical framework describing the interrelation between three key cultural factors that determine the quality and sustainability of cooperative outcomes. The acronym CRT stands for Communication (C), Relationship Management (R), and Trust (T). The model is based on scientific research[i], which demonstrates that the effects of cultural factors are well-established, and that all other factors influencing cooperation depend on the quality of these three core components.
Definition and Importance of Cooperation
Sociologists define cooperation as a fundamental[ii] aspect of societies and of interactions between organisms, groups, and communities. While selfish behavior exists in nature, species and systems that rely on cooperation and mutual support have historically prevailed. Conversely, purely egoistic strategies may lead to the elimination of partners or even the self-destruction of the actor.
The
success or failure of cooperation is determined by the perspectives, interests,
and actions of the participants. Ideally, cooperative efforts benefit all
participants; however, this is often the exception. In many cases, one partner
may dominate the interaction, sometimes resulting in the elimination or
absorption of the other. Examples of cooperative outcomes can be
observed daily in society, politics, business, and nature.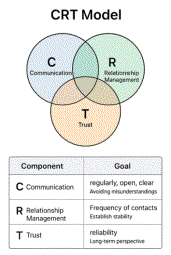
Core Components of the CRT Model
The CRT model identifies three critical and interdependent factors that determine the quality of cooperative interactions:
| Communication (C): Clarity, regularity, and openness of information exchange, which help avoid misunderstandings. | |
| Relationship Management (R): The ability to build, maintain, and nurture
personal and organizational relationships, establishing stability and mutual
understanding. | |
| Trust (T): Confidence in the reliability, integrity, and competence of partners, which enables sustained cooperation over time. |
Deficiencies in any of these components put cooperation at risk. While short-term successes may occur, sustained positive outcomes are unlikely without high-quality communication, robust relationships, and mutual trust.
![]()
Background
The CRT model was developed to address the influence of cultural factors on cooperation in both human society and nature. Traditional studies in sociology and organizational behavior often emphasized individual skills or structural conditions, but the CRT model integrates Communication, Relationship Management, and Trust as interdependent elements essential for successful cooperation i.
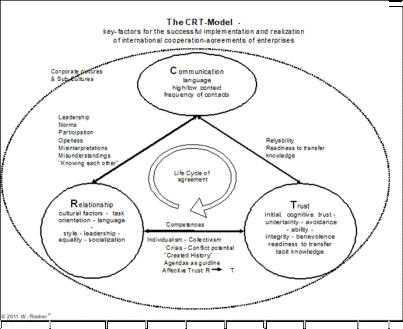 Research in cross-cultural psychology and organizational studies, including
the work of Geert Hofstede[iii]
and Robert Axelrod, demonstrated that cooperative behavior is shaped not
only by individual strategies but also by broader cultural norms and values.
Hofstede’s studies highlighted dimensions such as individualism versus
collectivism, power distance, and uncertainty avoidance, all of which influence
how people interact, communicate, and build trust. Axelrod’s analyses of
repeated interactions showed that strategies emphasizing cooperation and
reciprocity generally produce better long-term outcomes than purely
self-interested approaches.
Research in cross-cultural psychology and organizational studies, including
the work of Geert Hofstede[iii]
and Robert Axelrod, demonstrated that cooperative behavior is shaped not
only by individual strategies but also by broader cultural norms and values.
Hofstede’s studies highlighted dimensions such as individualism versus
collectivism, power distance, and uncertainty avoidance, all of which influence
how people interact, communicate, and build trust. Axelrod’s analyses of
repeated interactions showed that strategies emphasizing cooperation and
reciprocity generally produce better long-term outcomes than purely
self-interested approaches.
The CRT model synthesizes these insights, providing a framework for understanding why similar cooperative strategies may succeed in one cultural environment but fail in another. By focusing on the three critical factors—communication, relationships, and trust—the model offers a practical guide for enhancing cooperation in diverse contexts, including business, politics, and ecological systems.
![]()
Cultural Factors in the CRT Model
The CRT model emphasizes that the quality of the three core cultural factors—Communication, Relationship Management, and Trust—is decisive for the outcome of cooperation. While numerous cultural variables can influence interactions, scientific analysis shows that these three factors dominate the quality of all other influences on cooperative processes.
Other cultural dimensions, such as those identified by Hofstedeiii, affect the expression and effectiveness of CRT components:
| Individualism vs. Collectivism: Influences how relationships are managed and whether trust is extended primarily within a group or toward outsiders. | |
| Power Distance: Shapes communication patterns and the way trust is negotiated across hierarchical relationships. | |
| Uncertainty Avoidance: Affects how explicit communication and formalized agreements are used to establish trust. | |
| Masculinity vs. Femininity, Long-Term vs.
Short-Term Orientation, and Indulgence vs. Restraint: Further moderate cooperative strategies and
influence the implementation of CRT components. |
![]()
[i] Riether W., Cultural Integration as Key Factor, Saarbrücken ©2014 OmniScriptum, ISBN 978-3-639-679247-3
[ii]
Axelrod R., The
Evolution of Cooperation, Basic Books New York
©1984, ISBN 3-486-53993-0
[iii]
Hofstede's
cultural dimensions theory - Wikipedia
Hofstede, G.
(2001). Culture’s Consequences: Comparing Values, Behaviors,
Institutions and Organizations Across Nations. Sage Publications.